

Three weeks later, on May 5, 1961, Freedom 7 took off with astronaut Alan Shepard.
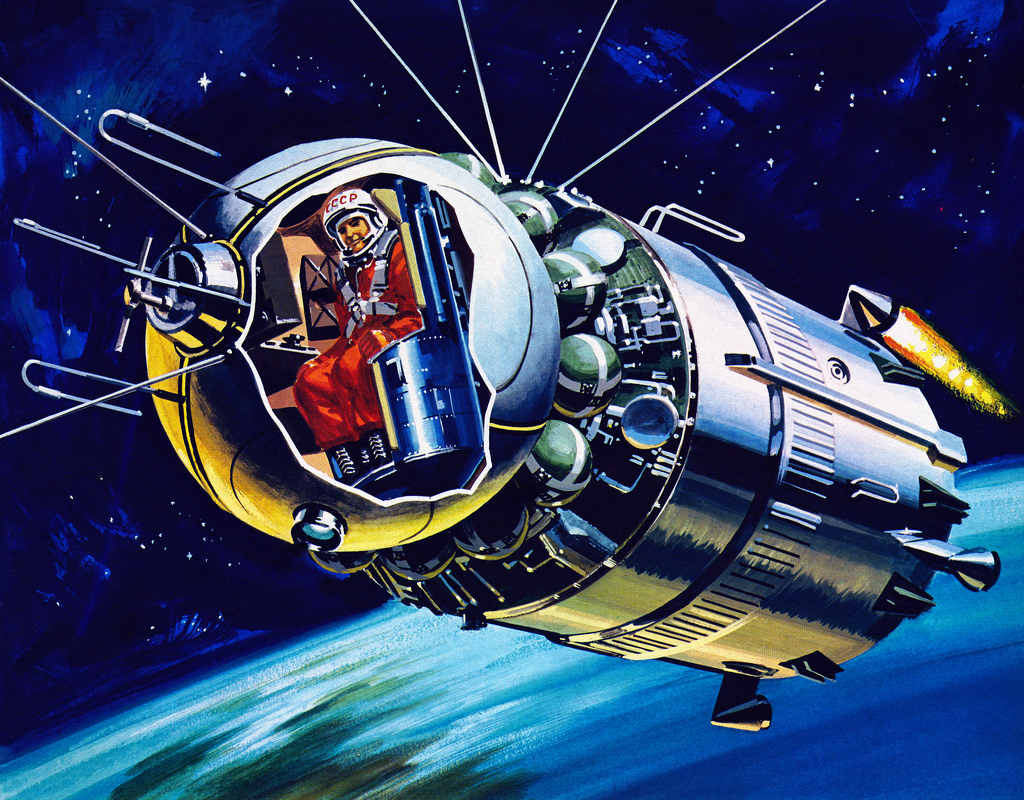
Vostok 1, with Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, orbited the Earth and returned safely. could get a man into space, something happened! On April 12, 1961, folks in the western hemisphere woke up to disconcerting news. Some people, including the astronauts, were ready to go, but Wernher Von Braun, the head of the Marshall Space Flight Center, felt that one more test flight ( MR-MD) was needed.

The last test flight caused some controversy.
MR-BD (“Booster Development”) flew on Maand reached an altitude of 113 miles. But the pilot was in satisfactory condition after landing. It flew higher and landed farther down range than expected. MR-2 was next with Ham, a chimpanzee as the “pilot”. It lifted off on Decemand reached a height of 130 miles and was weightless for over 5 minutes. All this is occurred while the capsule was still attached to the launch vehicle and sitting on the pad. With the escape tower gone, the capsule’s drogue, main, and backup parachutes all deployed, and the green die marker was released. However, it did so without taking the spacecraft with it. The escape tower fired and landed 400 yards away, which is what it’s supposed to do. The vehicle rose a few inches and settled back down on the pad. MR-1 was scheduled to take off on November 21, 1960. The next flights involved a Mercury capsule with a Redstone booster. However, the heat shield worked, and the test was considered a success. The capsule took off on an Atlas rocket that failed to push it to the desired height. There was also a Big Joe test of the Mercury Capsule heat shield on September 9, 1959. Little Joe 5, 5B and 6 flew with varying degrees of success. The passenger was another rhesus monkey, Miss Sam. Little Joe 1B followed a few weeks later on Janureaching a height of 9 miles. The passenger, rhesus monkey Sam, was weightless for over 3 minutes. Little Joe 2 lifted off on Decemand flew to a height of 53 miles and a distance downrange of 194 miles. The spacecraft took off and was recovered, although they were unable to test the escape tower. Little Joe 1A was a little more successful. Although, the escape tower worked as planned, it was supposed to fire after the spacecraft launched, not before. Then around a ½ hour before launch, the escape tower ignited pulling the capsule away and sending spectators scrambling. As the countdown proceeded, people were slowly moving to safe locations for the launch. Little Joe 1 was scheduled to launch on August 21, 1959. The first few unmanned test missions were launched from Wallops Island off the coast of Virginia using a booster called Little Joe. They were Scott Carpenter, Gordon Cooper, John Glenn, Gus Grissom, Wally Schirra, Deke Slayton, and Alan Shepard. After a rigorous selection process, the number was reduced to seven and the first astronauts were introduced to the nation at a press conference on April 9, 1959. The candidates had to be shorter than 5’ 11”, less than 40 years of age, and have a college degree. Astronauts would ride a small capsule (about the size of a small closet), be launched from the top of an ICBM ballistic missile, and, for the first time, fly above the Earth’s atmosphere.Īfter some deliberation it was decided that military test pilots would become the first astronauts. Therefore, in 1958, along came Project Mercury. It failed and became known by various names including “Flopnik” and my favorite “Stayputnik.” In late January 1958, the United States successfully sent Explorer 1 into orbit and the space race began.Īfter successfully launching its first few satellites, the United States decided it needed to move to the next stage and place humans (men) in space. The United States tried to follow in December 1957 with Vanguard TV-3. 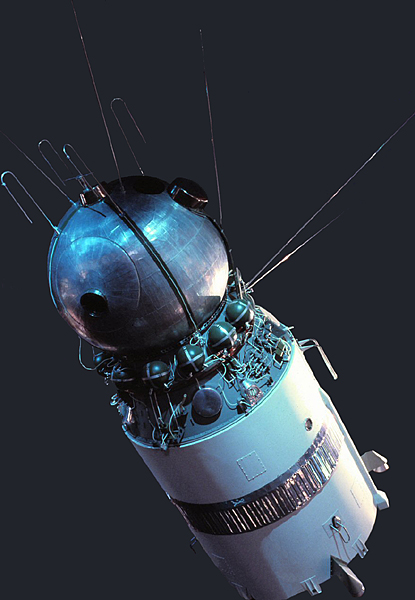
The impact of Sputnik, the first artificial satellite, resonated around the world. On October 4, 1957, a small round ball called Sputnik was launched into orbit by the Soviet Union. He did so as part of NASA’s Project Mercury. Sixty years ago this month (February 20, 1962), Astronaut John Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth. FAS Astronomers Blog, Volume 30, Number 2.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
